Precise regulation of particle size of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels: Measuring chain dimensions with a ‘‘molecular ruler”
Hui Xue a , Ziqing Zhao a , Rui Chen a, *(陈蕊), John L. Brash b , Hong Chen a, * (陈红)
a State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for Novel Functional Polymeric Materials, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, 199 Ren’ai Road, Suzhou 215123, P. R. China
b Department of Chemical Engineering and School of Biomedical Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 566 (2020) 394--400
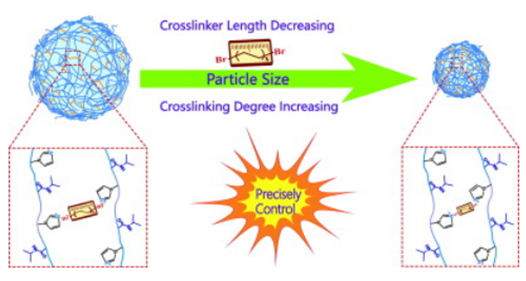
HYPOTHESIS Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels are used extensively in the design of drug carriers, surfaces for control of cell adhesion, and optical devices. Particle size is a key factor and has a significant influence in many areas. EXPERIMENTS In this work, precise control of the particle size of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels was achieved by controlling the separation distance of the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) chains. Dibromoalkanes of different size were used as an adjustable "molecular ruler" to measure molecular dimensions in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanoaggregates at the critical crosslinking temperature. FINDINGS We find that the chain separation distance decreases as the temperature increases with a sharp decrease over the 55-to-65 °C interval. Based on the observed relationships between chain separation and crosslinker, the particle size of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels can be regulated by changing the length of the "molecular ruler" (crosslinker) at the same temperature. Furthermore, for partly crosslinked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels that contain free crosslinkable sites, the particle size can be reduced still more by further crosslinking ("re-crosslinking") with crosslinkers of different size. It is shown that the particle size can be regulated by adjusting the length of "molecular ruler" and the degree of crosslinking. This work provides a "molecular level" method for precise control of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particle size.
链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979720300904