†, ‡, §, §, and † (黄小青)
† College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Jiangsu, 215123, China
‡ Department of Materials Science & Engineering, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China
§ Testing& Analysis Center, Soochow University, Jiangsu, 215123, China
Chem. Mater., 2016, 28 (12), pp 4447–4452
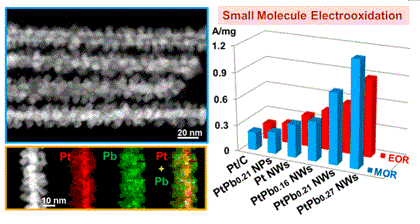
The development of highly efficient fuel cell devices is largely impeded by the limited electrocatalytic activity and stability of available Pt-based electrocatalysts. Herein, we report a facile one-pot strategy for the controlled synthesis of hierarchical Pt/PtxPb core/shell nanowires (NWs) with dendritic morphology. Different from the reported NWs, the present hierarchical core/shell NWs show the integrated features of one-dimensional (1D) structure, core/shell structure, alloy effect, and high surface area. These important characteristics enable them to be much more active and stable for methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) and ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR) than Pt NWs, the Pt-Pb nanoparticles (NPs), and commercial Pt/C (20 wt %, Pt particle size: 2–5 nm, Johnson Matthey) catalyst. Particularly, the present PtPb0.27 NWs are very stable in the MOR and EOR conditions with much lower activity decay after 1000 potential cycles than those of Pt-Pb NPs and the commercial Pt/C. This work highlights the importance of the precise control over 3D hierarchical structure in enhancing electrocatalysis for liquid fuel oxidations.
链接:http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01642