Tumor vessel-adaptable adhesive and absorbable microspheres for sustainable transarterial chemoembolization therapy
Jiakun Guo1,2,3, Jintao Huang4, Zuliang Huang1,2,3, Di Hu4, Hujing Tan1,2,3, Yan Wang1,2,3, Chao Deng1,2,3(邓超)*, Xiaoli Zhu4(朱晓黎)*,Zhiyuan Zhong1,2,3(钟志远)*
1Biomedical Polymers Laboratory, and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Functional Polymer Materials, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, and State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
2Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Functional Polymer Materials, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
3State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
4Department of Interventional Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6239
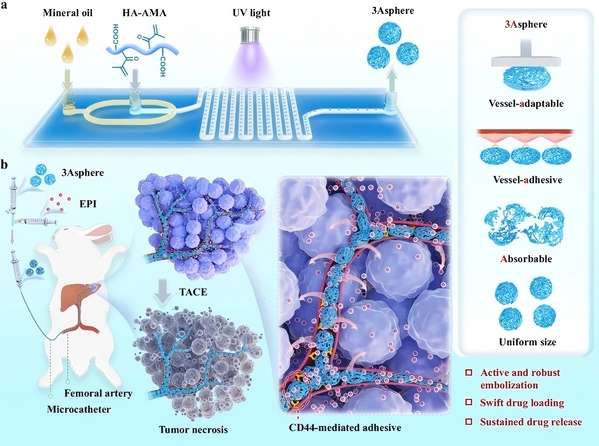
Abstract: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a common clinical intervention used for unresectable liver tumors, but conventional embolic microspheres generally exhibit slack vascular stacking and suboptimal drug release. Here, we report tumor vessel-adaptable, adhesive, and absorbable microspheres (3Asphere) based on hyaluronic acid developed using microfluidic and radical polymerization techniques for sustained TACE therapy of liver tumors. 3Asphere presents uniform sizes, gradual degradation over two months, and fast encapsulation and sustained release of chemotherapeutics such as epirubicin, irinotecan, and cisplatin. Interestingly, 3Asphere with high elasticity enables robust vascular embolization, effectively blocking rabbit renal blood supply for over one month. In rabbit VX2 orthotopic liver tumors, 3Asphere actively binds to endothelial cells via CD44 and inhibits tumor growth, affording significant survival benefits compared to commercial Embosphere®. TACE with epirubicin-loaded 3Asphere further enhances tumor inhibition and prevents lung metastasis. 3Asphere provides a versatile and advanced TACE therapy that might alleviate liver tumors.
Article information: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61621-4