Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
Modular Chiral Bisoxalamide−Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Oxo- Diels−Alder Reaction: Carbonyl Coordination for High Enantio- and Diastereocontrols
Jun-Bo Chen1, Man Xu2, Jun-Qi Zhang1, Bing-Bing Sun1, Jia-Ming Hu1, Jie-Qiang Yu1, Xing-Wang Wang1*(王兴旺), Yuanzhi Xia2*(夏远志), and Zheng Wang3*(王正)
1Key Laboratory of Organic Synthesis of Jiangsu Province, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, People’s Republic of China
2 College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang Province 325035, People’s Republic of China
3 State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032, People’s Republic of China
ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 3556--3563
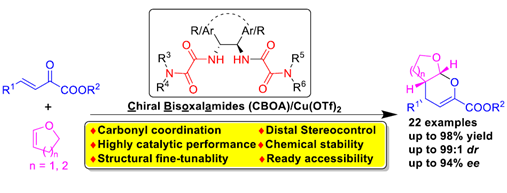
The chiral bis-oxalamides (CBOA), readily derived from optically pure 1,2-diphenylethylenediamine (DPEN), were proven to be a class of efficient C2-symmetric chiral ligands for copper(II)-catalyzed asymmetric inverse-electron demand oxo-Diels− Alder reactions between β,γ-unsaturated α-ketoesters and 2,3-dihydrofuran or 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran. The reactions proceeded smoothly under mild conditions to afford the corresponding [4 + 2] cycloadducts in high yields with good enantioselectivities (up to 94% ee) and diastereoselectivities (up to 99:1 dr). DFT calculations demonstrated that carbonyl coordination of the chiral ligand to Cu(II) was crucial for the high stereoinduction. These CBOA ligands exhibited high catalytic efficiency in this reaction, which
combined with some other salient features of structural fine tunability, chemical stability, and ready accessibility might endow more practical applications in asymmetric catalytic reactions.
链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acscatal.9b05606