Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
Highly Efficient Catalysts of Bimetallic Pt−Ru Nanocrystals Supported on Ordered ZrO2 Nanotube for Toluene Oxidation
Mengmeng Wang, Dongyun Chen*(陈冬赟), Najun Li, Qingfeng Xu, Hua Li, Jinghui He, and Jianmei Lu*(路建美)
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2020,12, 13781--13789
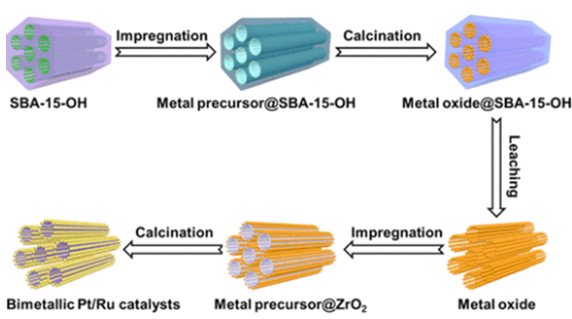
ZrO2 nanotube arrays and their supported bimetallic platinum and ruthenium (PtxRuy/ZrO2; x + y = 1 mmol %, x/y = 1:0, 0.9:0.1, 0.8:0.2, 0.7:0.3, 0.5:0.5, 0:1) nanocomposites were fabricated by employing SBA-15-OH as a hard template and an impregnation method, respectively. A controlled ordered nanotube array structure formed from the fabricated catalysts, and it showed a good performance for toluene oxidation. The specific physicochemical properties of the catalysts were examined through various analytical means. The PtxRuy/ZrO2 possessed a high surface area, and the Pt–Ru nanoparticles were dispersed uniformly on the ZrO2 nanotube surface. The Pt0.7Ru0.3/ZrO2 catalyst performed best among all of the samples, with T90% and T100% (temperatures for 90 and 100% conversion of toluene) of 140 and 160 °C, respectively, at a weight hourly space velocity of 36 000 mL/(h·g). These bimetallic catalysts exhibit excellent characteristics for toluene oxidation, such as higher turnover frequencies and lower apparent activation energy (Ea) values, which probably result from the synergistic effect of the Pt–Ru noble metals that leads to a high reducibility and oxygen adsorption capacity. The excellent activity, stability, and economics of the Pt0.7Ru0.3/ZrO2 catalyst allow for its application in toluene removal.
链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.9b20929