Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
From bimetallic PdCu nanowires to ternary PdCu-SnO2 nanowires: Interface control for efficient ethanol electrooxidation
Tongxin Song, Fei Gao, Liujun Jin, Yangping Zhang, Cheng Wang, Shujin Li *(李淑瑾) , Chunyan Chen, Yukou Du *(杜玉扣)
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, 199 Renai Road, Suzhou 215123, PR China
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 560 (2020) 802--810
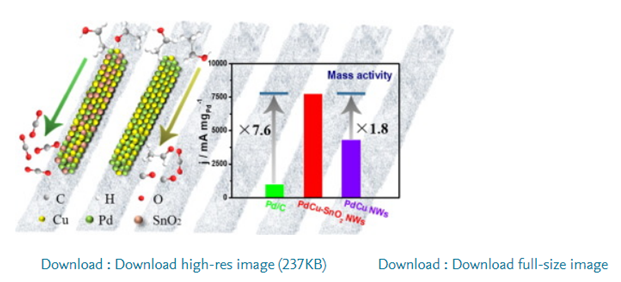
At present, although a large number of palladium-based nanowire electrocatalysts have been prepared, there are few reports on nanowires containing rich metal oxides. Herein, porous PdCu alloy nanowires and PdCu-SnO2 nanowires were prepared by using a galvanic displacement synthesis method. Due to their one-dimensional structure, rough surfaces with non-homogeneous edges, electronic effect, and the advanced PdCu/SnO2 interface of the as-synthesized PdCu-SnO2nanowire catalysts, they exhibited a mass activity of 7770.0 mA mg−1 towards ethanol oxidation, which was 7.6-fold higher than that of Pd/C catalysts (1025.0 mA mg−1). In addition, they behaved strong durability upon chronoamperometry and continuous cyclic voltammetry tests. The electrochemical measurements demonstrated that SnO2 was introduced into the PdCu/SnO2 interface, which promoted the oxidation of ethanol at a lower potential and accelerated the oxidation of Pd-COads via SnO2-OHads to regenerate the active sites. This research highlights the significance of introducing metal oxides into the nanostructure interface, and the performance of Pd-containing catalysts towards ethanol oxidation reaction was greatly improved.
链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021979719313256?via%3Dihub