Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
High-Voltage Resistant Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Haojun Qi†, Yongyuan Ren†, Siyu Guo†, Yuyue Wang‡, Shujin Li‡, Yin Hu†, and Feng Yan*,† (严锋)
† Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123, China
‡ College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123, China
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 591--600
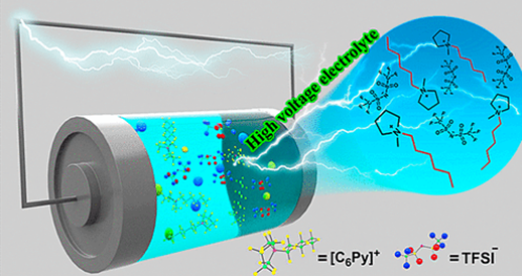
With the growing demand for high energy and high power density rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, increasing research is focused on improving the output voltage of these batteries. Herein, a series of pyrrolidinium and piperidinium cations with various N-substituents (including cyanomethyl, benzyl, butyl, hexyl, and octyl groups) were synthesized and investigated with respect to their electrochemical stability under high voltages. The influence of substitutions at the N-position of pyrrolidinium and piperidinium cations on their high-voltage resistance was studied by both theoretical and experimental approaches. The voltage resistance was enhanced as the electron-donating ability of the substitutes increased. Furthermore, 1-hexyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide ([C6Py][TFSI]) exhibited the highest decomposition voltage at approximately 5.12 V and showed promising potential in a lithium-ion battery.
链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.9b16786