Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
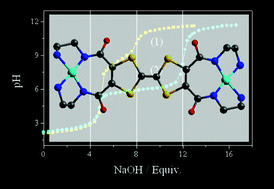
A bis(diamino-diamido) tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) derivative H4L2 has been designed and synthesized. Experiments of pH titration reveal that integrating the redox active TTF unit with the diamino-diamido moiety adds new properties to the traditional ligand. Oxidation of the TTF moiety increases the acidity of the amido group, and the coordination of metal ions is also sensitive to the oxidation state of the ligand. This compound is capable of acting as a leaving or accepting ligand for proton and metal ions. The electrochemistry of the protonated TTF derivative of H4L2 was studied in the presence of a series of oxo anions and metal cations. The results indicate that the redox potentials selectively respond to HC2O4− and SO42− anions, and Ni(II) and Cu(II) cations. Solid-state structures of a cation–anion salt H8L2·2SO4·8H2O and a nickel coordination compound [Ni2L2]·2DMF have been characterized by means of X-ray crystallography which are helpful in understanding the inter-ion interactions.