Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
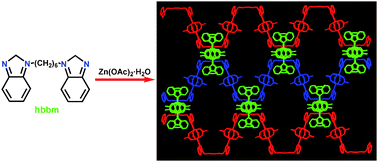
Solvothermal reactions of 1,1′-(1,6-hexanediyl)bis-1H-benzimidazole (hbbm) with Zn(II), or Cd(II) salts yielded six coordination polymers, [MX2(hbbm)]n (1: M = Zn, X = Cl; 2: M = Zn, X = Br), {[CdI2(hbbm)]·0.5H2O}n (3), [CdCl2(hbbm)2]n (4), [Cd3(η,μ-OAc)2(μ-OAc)2(OAc)2(hbbm)2]n (5), and [Zn2(μ-OAc)4(hbbm)]n (6). Compounds 1–6 were characterized by elemental analysis, IR, powder X-ray diffraction, and single crystal X-ray diffraction. Compounds 1–3 contain a 1D zigzag chain in which [MX2] units are linked by hbbm bridges. For 4, each [Cd4Cl8(hbbm)4] unit acting as a planar four-connecting node connects other four equivalent ones via eight hbbm molecules to form a 2D (4,4) network. For 5, each linear [Cd3(η,μ-OAc)2(μ-OAc)2(OAc)2] unit is linked by two pairs of hbbm bridges to afford a 1D double chain. For 6, each [Zn2(μ-OAc)4] unit is connected by hbbm bridges to form a 1D U-type chain, which further interweaves with other adjacent chains to form a unique 3D net. The solid state luminescent properties of 1–6 at ambient temperature were also investigated.