Welcome to College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science of Soochow
University
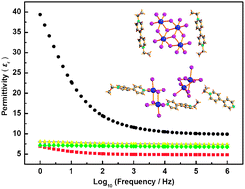
The solvothermal reactions of BiI3, KI, I2, 4,4′-bipyridine (4,4′-bipy), and a small amount of water in alcohol and acetonitrile produced four bipyridinium iodobismuthates {[MQ]3[Bi2I6(μ-I)3][Bi2I6(μ-I)2(MQ)2]3} (1, MQ+ = N-methyl-4,4′-bipyridinium), {[EQ]3[Bi2I6(μ-I)3][Bi2I6(μ-I)2(EQ)2]3} (2, EQ+ = N-ethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium), [MV][BiI5] (Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2010, 5326) (3, MV2+ = N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium), and [EV]2[Bi4I10(μ-I)4(μ3-I)2] (4, EV2+ = N,N′-diethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium). In these reactions, 4,4′-bipy was partly or completely alkylated by alkyl groups generated from the cleavage of C–O bond of alcohols, forming the N-alkyl-4,4′-bipyridinium cation (Q+) and the N,N′-dialkyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dication (V2+), respectively. Compounds 1–4 were characterized by elemental analysis, IR, 1H NMR and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The optical, electrical conductive and dielectric properties of these compounds were investigated. The dielectric constants of the Q+-based compounds were larger than the values of the V2+-based ones, which showed that the weak electrostatic interactions in the structures may benefit the polarizability of molecules, thereby resulting in a larger dielectric response of the structures under an external electric field, while the strong electrostatic interactions between the positive and negative charge units would lead to a low dielectric constant (low-k) behavior of these compounds.